
Notice how the logarithmically-spaced contours (at 1, 10, 100, and 1000) show the lower-level variability without "saturating" the higher regions with contour lines. Notice how the 1ppm contour map shows the spatial variations within the lower levels while the 1000ppm map does not.Ĭompare the regularly-spaced contours in the diagrams above with the logarithmically-spaced contour maps below.
#Contour interval series
These maps depict this data set as a series of conventional, regularly-spaced contour maps. Specifically, the bulk of the model is made up of values between zero and 200 while the anomalous regions exceed 10,000ppm. The maps below depict a grid model that is grossly skewed by some very high values. geochemistry with a high range of z-values). This option is useful for plotting data that not well suited for conventional, regularly-spaced contouring (e.g. Logarithmic (Base-10): Choose this option to draw the contour lines at logarithmically-spaced intervals.Note: The labeled contour interval must be a multiple of the unlabeled contour interval. Confirm Intervals: If checked, the program will let you confirm/override the suggested contouring and labeling intervals prior to creating the contour map.For example, if the data ranges from 10 to 100, the program might choose a contour interval of 10 and the contours would be plotted at the following levels: 10 20 30, 40., 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, and 100. Regular: Choose this for the program to draw contour lines at regularly-spaced intervals, which the program will determine automatically.Intervals: Choose from regularly-spaced, logarithmic, custom, or manually-defined contour intervals.Contour Lines are also available for display on solid model profile and section panels to represent G-value distribution.Ĭheck this box to turn on the Contour Lines layer in your map or diagram.Ĭlick on this tab to establish the contour options. It is used to represent the distribution of z-values (elevations, concentrations) throughout the study site using line contours. The Contour Lines layer is offered in many RockWorks map windows. This will provide accurate estimates of elevation and slope, and subsequently improve the analyses that rely on these digital derivatives.Contour Line Options Contour Line Options For areas with variable terrain complexity, the suggestion is to generate DEMs and slope at a suitable resolution for each terrain separately and then to merge the results to produce one final layer for the whole area. The implementation of the models will guide users to select the best combination to improve the results in areas with similar topography. The effect of these factors on the accuracy of the DEM and the slope derivative was quantified using models that determine the level of accuracy (RMSE). The study indicated different alternatives to achieve an acceptable accuracy depending on the contour interval, the DEM resolution and the complexity of the terrain. This research investigates the effect of sampling density used to derive contours, vertical interval between contours (spacing), grid cell size of the DEM (resolution), terrain complexity, and spatial filtering on the accuracy of the DEM and the slope derivative. The accuracy of such DEMs depends on different factors.
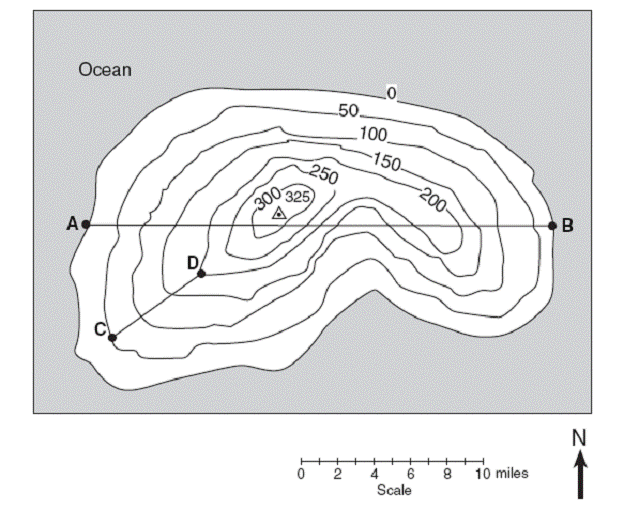

DEMs are frequently derived from contour lines. Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) are indispensable tools in many environmental and natural resource applications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
